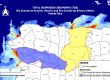
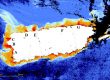
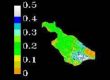
Variations of total suspended sediment (TSS) in Mayagüez Bay and their relationship with inland soil erosion rates were the main objectives of the research conducted by Vilmaliz Rodriguez. In December 8, 2009, she presented the results of her work and successfully defended her thesis. Several analyses were developed using in situ remote sensing reflectance, backscattering, and TSS data collected on research cruises carried out between January 2004 and October 2006. The field data were compared with images from MODIS. The analyses identified the range between 589 nm to 645 as the target spectral region to estimate TSS, and showed the potential of using red to green ratios to improve these estimations. This study incorporated an innovative methodology which used satellite derived TSS products to estimate suspended sediment load in order to compared coastal variation with inland soil erosion estimations. Geographic Information Systems techniques were incorporated in this analysis by applying the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) to Mayagüez Bay watershed. Results of this study represent an important advancement in the development and application of Remote Sensing and GIS based studies in tropical coastal waters.

Category: Students