In pharmaceutical industry there are processes which are very important and play a crucial role in some stages of manufacture, they include blending or mixing operations. In the case of mixing the goal is to achieve the same quantity in the dosage unit, as also to obtain a homogeneous association of several solid products. When there is a system that contains particles with different properties (size, density, or shape) a critical problem appears due to segregation which will impact in the final quality of the product. Thus, the main challenge will be to maintain as much as possible the homogeneity in the blend.
Pharmaceutical dosage forms could be analyzed by using techniques which can offer 2D or 3D images in order to see much better all their properties. X-ray tomography is a new approach to imaging the internal structure of solid dosage forms. This technique is nondestructive that has a high penetration ability and provides a reasonable level of resolution. Nowadays, computed tomography is most frequently employed using X-rays. Due to the high energy that is used to generate the X-rays, they have the advantage of being capable to penetrate easily all pharmaceutically relevant excipients; high resolution images can be obtained because the short wavelength and the negligible diffraction.
It should be mentioned that must be chosen material that generates sufficient X-ray contrast, then it is feasible to determine the distribution of the active ingredient or functional excipient.
There are several software that serve to perform tomography reconstructions, they have sets of algorithms which permit reconstruct the images that were taken in 2D and then create the 3D ones. Gray scale images also could be manipulated using image analysis techniques to produce binary or multiple-colored images and to obtain dimensional information about the sample.
There are previous works that have been developed for different applications using X-ray tomography. Patrick Wray et al. used X-ray microtomography technique to reconstruct 3D spatially resolved images of materials with different density.
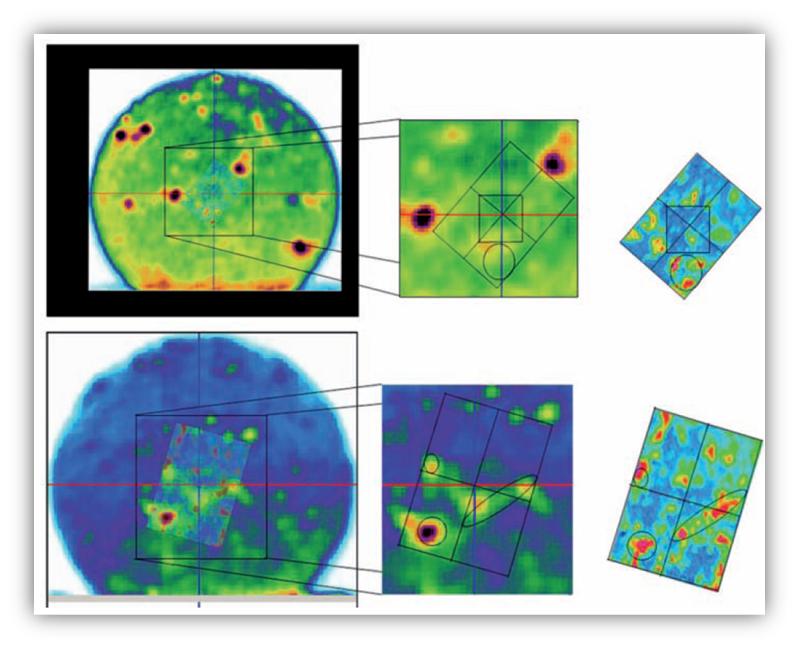
 Figure 1. FTIR spectroscopy compared with X-ray microtomography images. The FTIR (right hand side). The key area of the X-ray tomography (middle) and the FTIR is layered over the X-ray data for comparison (left hand side).
Figure 1. FTIR spectroscopy compared with X-ray microtomography images. The FTIR (right hand side). The key area of the X-ray tomography (middle) and the FTIR is layered over the X-ray data for comparison (left hand side).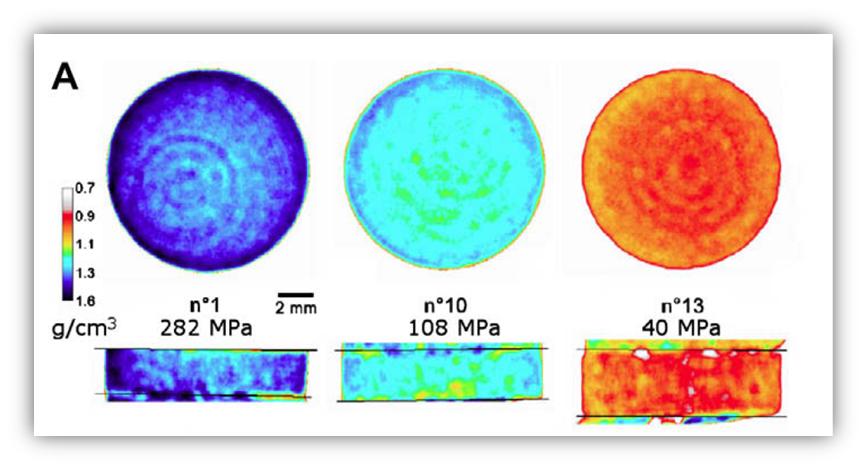
Figure 2. X-ray microtomography applied to pharmaceutical cylindrical tables at different compaction pressures.
In conclusion, X-ray Tomography serve to determine the powder mixture distribution that can be obtained after reconstruct the images with specialized softwares, then a quantitative information about the distribution and homogeneity in the pharmaceutical samples (tablets) is acquired.
By Merlis P. Alvarez-Berrios
